You are on CGS' Legacy Site.
Thank you for visiting CGS! You are currently using CGS' legacy site, which is no longer supported. For up-to-date information, including publications purchasing and meeting information, please visit cgsnet.org.

By Hironao Okahana and Christian P.L. West
According to the Council of Graduate Schools (CGS), applications for admission to master’s programs increased by 1.4% and for doctoral programs by 4.1% between Fall 2017 and Fall 2018, while first-time enrollment in these programs grew by 2.0% and 2.9%, respectively (Okahana & Zhou, 2019a). Despite recent declines in international graduate enrollment (Okahana & Zhou, 2019a & 2019b), overall graduate enrollment at U.S. colleges and universities continues to grow, albeit modestly. This is not surprising as workforce demands for graduate degree holders are still growing in the United States. Jobs that require master’s degrees and doctoral degrees at the entry are expected to rise by 13.7% and 9.0% between 2018 and 2028, respectively (U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2019).
To gain insights about how graduate schools and programs are working to respond to this growing need for graduate degree holders, CGS collaborated with NAGAP, the Association for Graduate Enrollment Management to survey graduate enrollment management (GEM) professionals at U.S. and Canadian based institutions. Of the 167 respondents to the survey, 47.3% of GEM professionals reported that their institution or program has a robust enrollment growth target - 10% or more. In this brief, we discuss some of the insights gathered from this survey of GEM professionals.
Key Findings
- In addition to the national labor market and workforce demands, GEM professionals in the survey whose units have robust enrollment growth targets cited the importance of the reputation and ranking of the program/institution; availability of scholarship/fellowships; and campus/program climate as factors influencing decision to grow. The importance of these factors varied by specific institutional characteristics, including the Carnegie classification and public-private status. For example, regional and local labor market and workforce needs were more important at public institutions than their private counterparts. (Figure 1)
Figure 1.
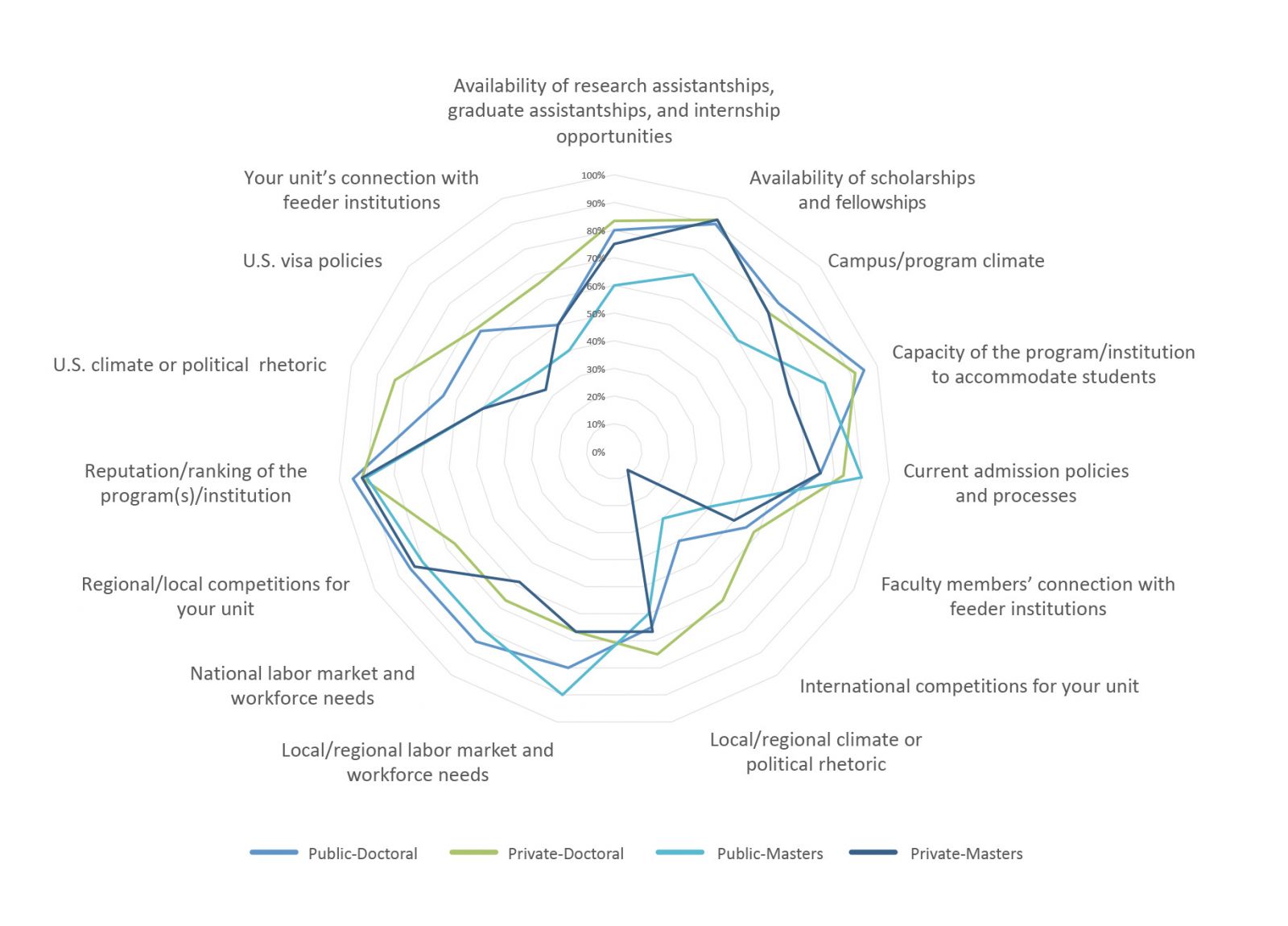
Data Source: NAGAP, The Association for Graduate Enrollment Management & Council of Graduate Schools, Survey of Graduate Enrollment Management Professionals, Summer 2019.
- GEM professionals also cited increased resources such as additional full-time professional staff, implementation of a customer relations management system, institution-wide enrollment management strategy, and a dedicated budget for marketing and travel as critical to their ability to meet enrollment goals. (Table 1)
Table 1.

- Also, GEM professionals identified the reputation of the program/institution, campus climate, admission policies, and resources for recruitment as the top factors in their ability to increase the diversity of their incoming student body. (Figure 2)
Figure 2.
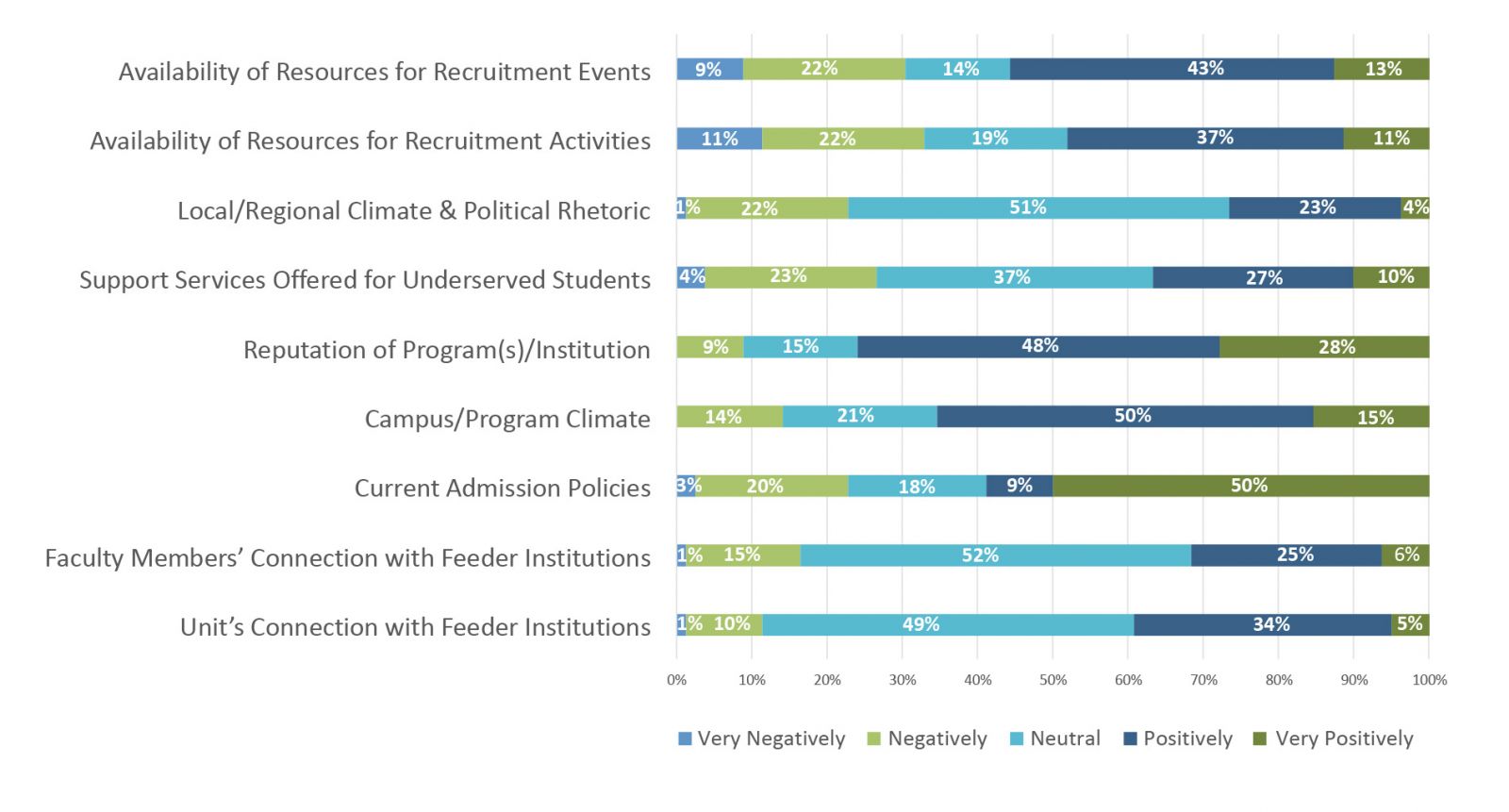
Data Source: NAGAP, The Association for Graduate Enrollment Management & Council of Graduate Schools, Survey of Graduate Enrollment Management Professionals, Summer 2019.
Takeaway Points
- Internal and external factors contribute to the setting of robust enrollment increase targets. There are both push and pull factors between program/institutional strengths and national, regional, and local workforce demands. This underscores the importance of aligning the strength of graduate programs with national, regional, and local labor market needs.
- In qualitative survey responses, GEM professionals make a direct connection between enrollment goal setting and institutional infrastructure. The alignment of goals and resources may increase confidence among GEM professionals in their ability to achieve their enrollment goals.
- While GEM professionals have confidence in their ability to achieve their overarching graduate enrollment goals for their units, they acknowledge meeting diversity goals as a different challenge. Given the positive influence of the reputation of institutions and graduate programs, as well as campus climate cited by GEM professionals, successful diversity recruitment strategies appear to require broader participation of stakeholders beyond GEM professionals.
Conversation Starters for Graduate Deans
- How do your graduate school and graduate programs use local, regional, and national workforce projections to determine enrollment goals?
- What resources can your graduate school and graduate programs leverage to meet the enrollment goals for specific segments of the recruitment pipeline,e.g., masters, doctoral, professional, domestic, international?
- What strengths can your graduate school and graduate programs leverage to successfully recruit a more diverse graduate student population in recruitment? How do diversity goals align with overall enrollment goals, strategies, and resource allocations?
Additional Resources
- Graduate Enrollment Trends: CGS/GRE Survey of Graduate Enrollment and Degrees and CGS International Graduate Admission Survey provide yearly snapshots and trends in graduate applications and enrollment across all fields of master’s and doctoral programs. Beyond the published report, requests for custom data reports can be made to CGS.
- The Outlook of the Workforce Needs: O*NET OnLine is an online tool for career exploration and job analysis sponsored by the U.S. Department of Labor. The web tool offers detailed insights, including projections of workforce needs and education and training needs for each occupation by the Standard Occupational Classification. Additional data may also be available via state and regional workforce development boards.
- Guides for Holistic Graduate Admissions: Two recent CGS projects: Innovation in Graduate Admissions through Holistic Review (supported by Hobsons) and Master’s Admission Attribute Study (supported by ETS) offer insights for promising practices in graduate admissions and enrollment management. NAGAP, The Association for Graduate Enrollment Management also offers the Holistic Admissions Resource Guide, as well as there are other efforts, such as Inclusive Graduate Education Network offers workshops for inclusive admissions practices.
References:
Okahana, H., & Zhou, E. (2019a). Graduate enrollment and degrees: 2008 to 2018. Washington, DC: Council of Graduate Schools.
Okahana, H., & Zhou, E. (2019b). International graduate applications and enrollment: Fall 2018. Washington, DC: Council of Graduate Schools.
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. (2019). Table 5.2 Employment, wages, and projected change in employment by typical entry-level education (Employment in thousands). Retrieved from https://www.bls.gov/emp/tables/education-summary.htm.
About the Data Source:
The 2019 NAGAP/CGS Survey of Graduate Enrollment Management Professionals was developed by CGS, in consultation with NAGAP, and sent out to NAGAP members throughout July – August 2019. This brief is based on the deidentified, individual-level data file of 167 respondents. 91% of respondents voluntarily identified their institution and institutional characteristics were added to the data file using 2015 Carnegie Classification information. Analysis for this brief is based on a sample of 47.3% (N=79) institutions identifying a goal to increase overall enrollment by 10% or higher. These institutions break out into public Doctoral institutions (N=20), private Doctoral (N=12), public Masters institutions (N=10), and private Masters institutions (N=10).
Author Contribution and Acknowledgment
The brief was prepared by Hironao Okahana and Christian P.L. West. H.O. conceived and designed the project and data collection instrument, as well as supervised the analysis for this work. C.W. performed data cleaning and analysis, prepared the figures and table. Both authors discussed and contributed to the final brief. Suzanne T. Ortega, Enyu Zhou, Radomir Ray Mitic, and Janet Gao also provided feedback to earlier drafts of the brief. NAGAP, The Association for Graduate Enrollment Management provided feedback to earlier versions of the data collection instrument and administered the survey to its members. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this brief do not necessarily reflect the views of NAGAP.





